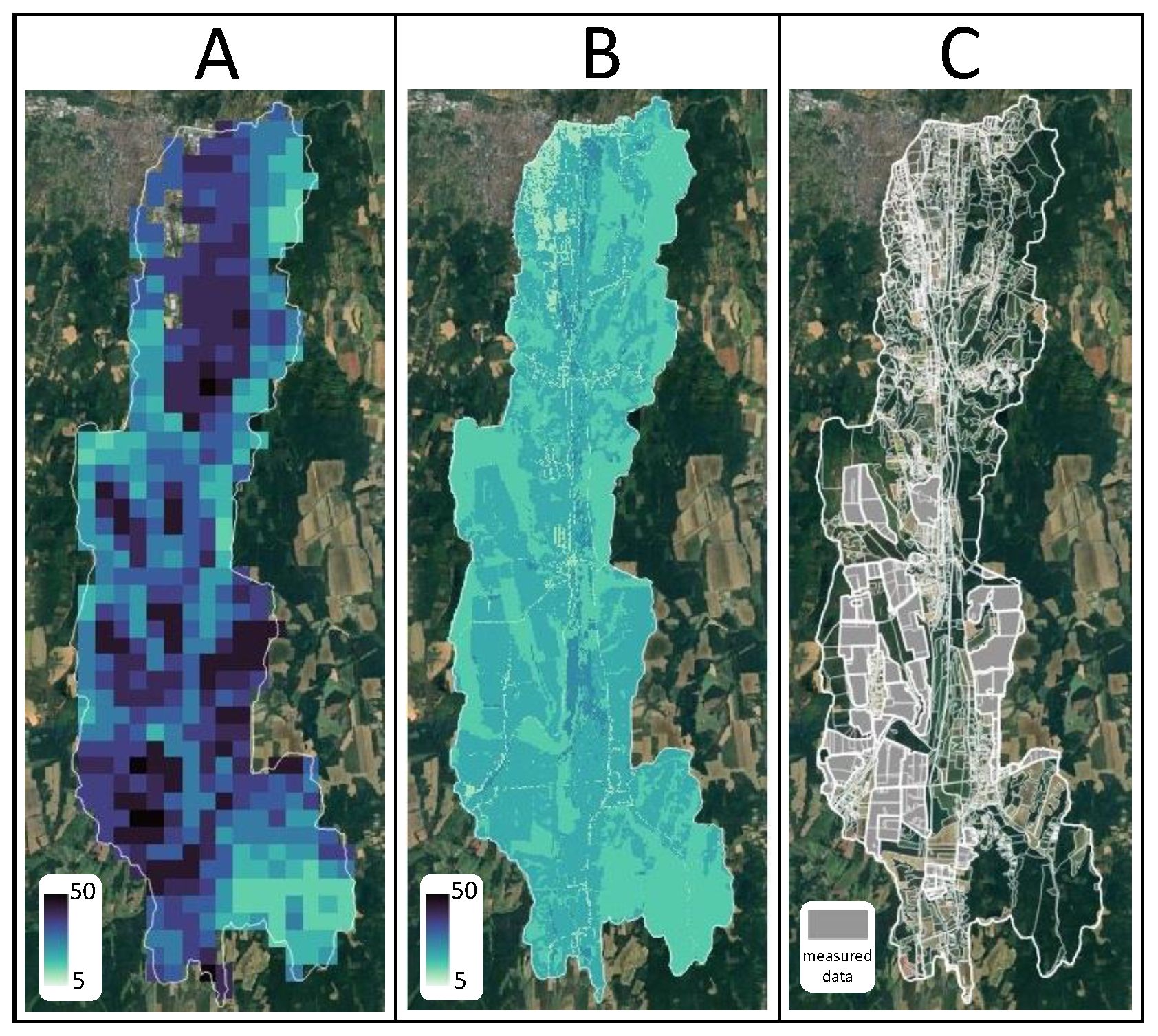
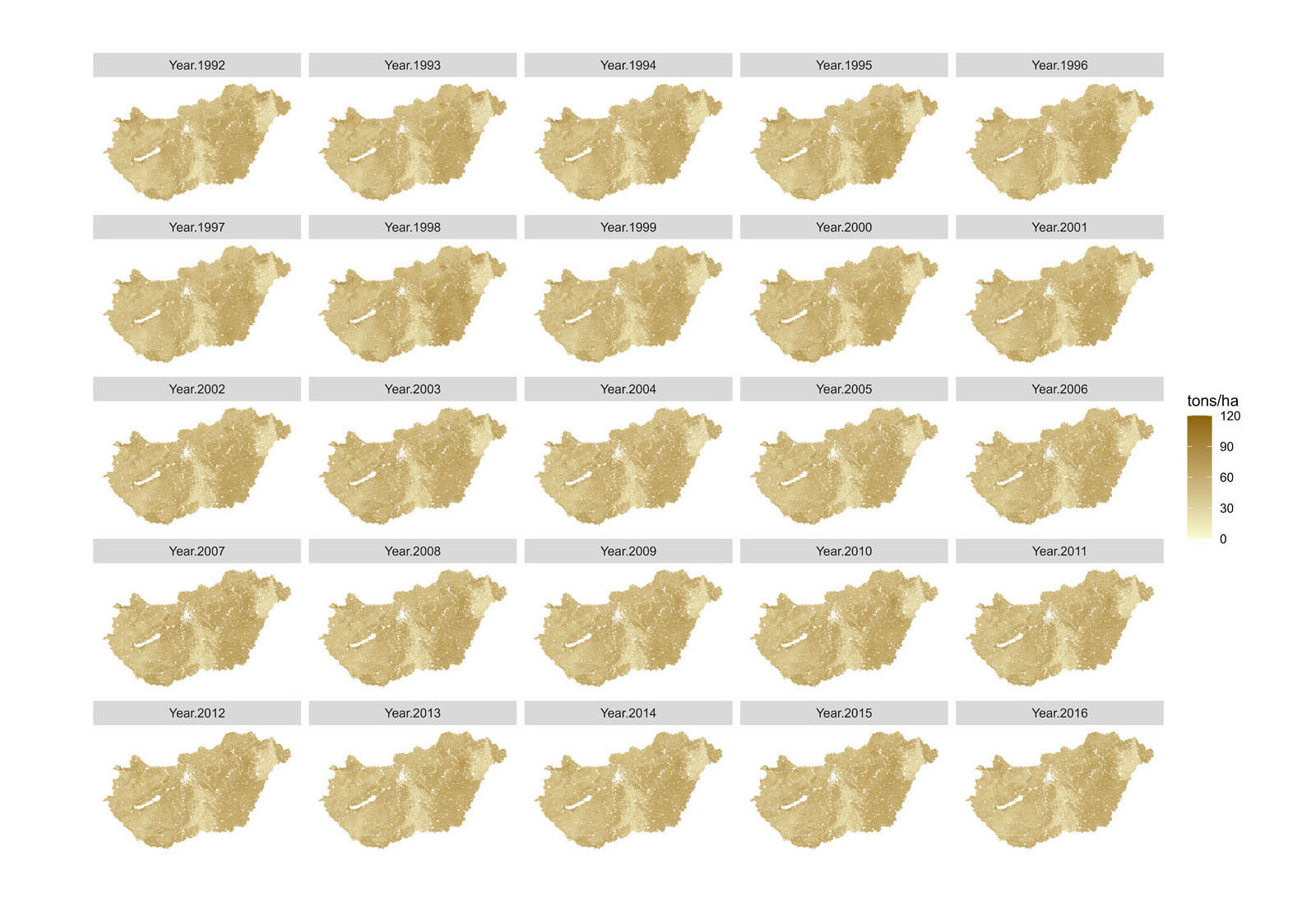
The presented methodology stands out by using a hybrid approach that integrates machine learning with space-time geostatistics, addressing key limitations of previous approaches. It allows for reliable SOC predictions along with uncertainty estimates at any spatial and temporal scale, even in years where no direct SOC measurements are available. This comprehensive method offers a more robust and dynamic understanding of SOC changes not just in space but also in time. The compiled map series provide valuable information for researchers, society and even policymakers, helping to tackle environmental challenges such as land and soil degradation, climate change, and ecosystem assessment. These findings support ongoing initiatives like the EU Soil Monitoring Directive and the UN Sustainable Development Goals, offering practical tools for tracking SOC changes and assessing soil health over time.
This research fills a key gap in our understanding of SOC dynamics in Hungary and offers a methodology that can be adapted internationally to improve the accuracy and utility of SOC data to address the environmental challenges and crises of our time.